Healthy weight gain during pregnancy plays an important role in the health of all pregnant women and their babies, including reducing the risk of maternal and neonatal complications, such as pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, low or high birth weight and improving breastfeeding outcomes such as increasing the rates of breastfeeding initiation. The amount of weight gained during pregnancy can also impact the long-term health of both the mother and the baby. There is some evidence to suggest that excessive weight gain during pregnancy can increase the risk of asthma exacerbations (Jensen et al. 2021, Ali et al. 2018)
Recommended gestational weight gain (GWG) is determined based on the individual’s pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) (Institute of Med. & National Research Council 2009). This is calculated as body weight (in kilograms), divided by the square of height (in metres). It is recommended that height and weight are measured at the first antenatal visit to determine pre-pregnancy BMI, unless an accurate record is available (Dept. Health 2020), with continued monitoring through pregnancy.
Pregnancy weight gain calculator
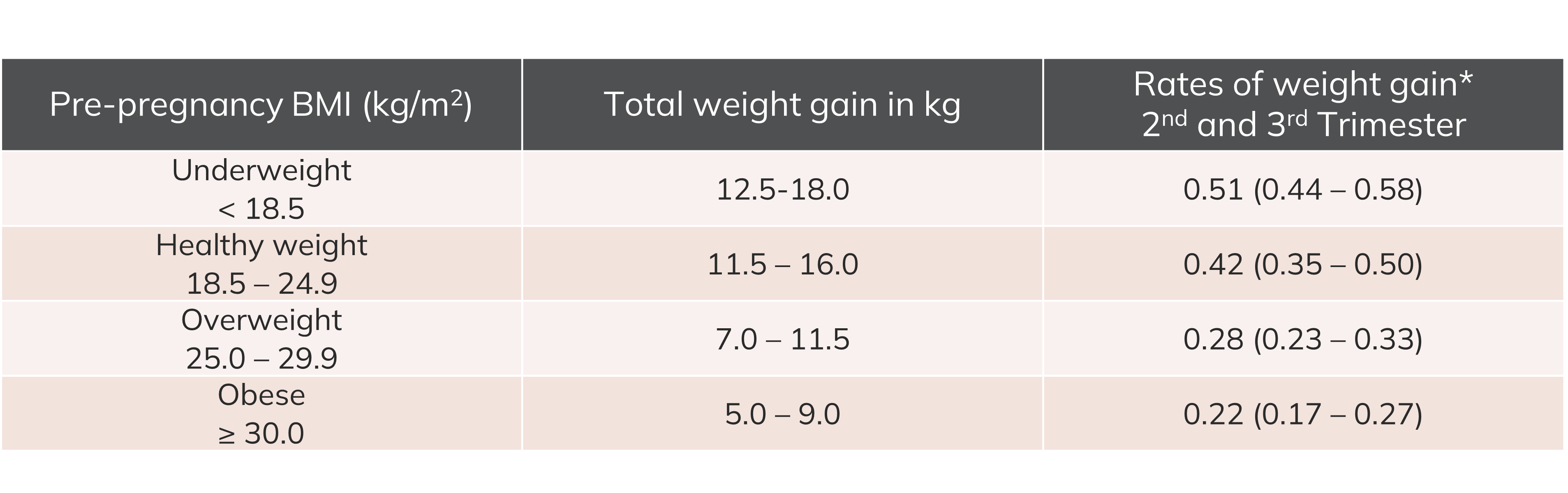
Recommendations for total and rate of weight gain during pregnancy, by pre-pregnancy BMI. Adapted from the 2009 Institute of Medicine guidelines. BMI: body mass index. *Calculations assume a 0.2-2kg weight gain in the first trimester. Note: these recommended weight gain ranges are intended to be used as suggested limits rather than specific goals and may not be applicable to all women for example those from an Asian background.
Excessive GWG is observed in almost 50% of general pregnancies, with only one-third of women estimated to gain the weight within the recommended ranges during pregnancy (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2016). Women with asthma have been reported to be at greater risk of weight gain during pregnancy and more likely to retain weight postpartum compared to the general population (Stevens et al. 2021).
Approximately 7 in 10 women with Asthma gain more weight than is recommended during pregnancy, regardless of their weight category (Jensen et al. 2020). This highlights the importance of educating women with asthma about the importance of healthy weight gain during their pregnancy and supporting them in gaining the recommended amount of weight through relevant resources and a referral to an Accredited Practicing Dietitian as appropriate.
Recommendations
Currently, there are no specific dietary guidelines for pregnant women with asthma. Therefore, the following recommendations from The Clinical Practice Guidelines: Pregnancy Care (2020) around monitoring and supporting healthy gestational weight gain and promoting healthy eating should be followed in the management of pregnancy in asthma (Department of Health 2020).
- Explain the purpose of assessing weight and weight gain during pregnancy
Pre-pregnancy BMI and GWG are important determinants of the health of both the mother and the baby. Women planning a pregnancy should be advised about the benefits of having a weight within the healthy range before pregnancy, as well as the importance of meeting the recommended healthy GWG for their pre-pregnancy BMI throughout pregnancy.
- Engage women in discussions about weight gain
Women should be offered the opportunity to be weighed at each antenatal appointment so that weight gain outside the recommendations and the risk of associated adverse outcomes can be identified and monitored.
- Make weight assessment routine
Just like other measures of baby’s growth, taking mum’s weight can be presented as part of routine/comprehensive monitoring of their progress. Aim to use the same scales to weigh the woman at each antenatal visit and, if appropriate, ask the woman to remove shoes and any heavy items e.g. belts.
Most women are happy to have their weight measured (Allen-Walker et al. 2017). Women may wish to track their weight using the NSW government Get Healthy in Pregnancy Weight Gain calculator (printable information here).
While it is important that weight gain is within the recommended range for their BMI category, the goal is for mother and baby to be receiving all the nutrients required for healthy growth and development. Weight loss during pregnancy should be avoided. Weight loss through food restriction/dieting in particular can result in the baby not receiving adequate nutrients for proper growth and development.
Learn more about healthy eating advice for pregnant women here.
- Consider referral to an Accredited Practicing Dietitian
Referral to an Accredited Practice Dietitian for individualised nutrition advice should be considered for women with a BMI outside the healthy range, or who are gaining gestational weight above or below the recommended range for their pre-pregnancy BMI, or for whom there may be dietary concerns/risk factors. Women who are losing weight should undergo further assessment (e.g. hyperemesis) and consider referral to an APD.
Find an APD here.
